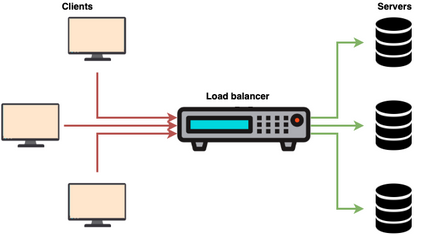
What is load balancing?
Load balancing is a technique consisting in sharing the load between several servers in the same cluster. When the number of users increases, the web performance is reduced except when using a load balancer. This technique is also used in networks to share traffic between several physical lines and even in computers, servers with several processors and/or several hard disks.
What is the purpose of load balancing?
The purpose of a load balancer is to:
- Firstly, improve processing time of requests.
- Secondly, ensure the high availability (HA) of the platforms, to overcome the failure of one or more machines.
- Then, provide the ability to add new servers to the cluster without downtime.
How does load balancing work?
A load balancer performs regular checks to ensure the proper functioning of the farm’s servers. As a result, the load balancer determines the servers to which the requests will be redirected to. We can use this in web hosting in order to achieve the desired web performance.
Which distribution algorithm to use?
When setting up a load balancer, the administrator must choose a distribution algorithm according to the desired web performance and the available hardware. Below are the most famous algorithms:
- Round Robin (Fair sharing of requests between servers)
- Weighted Round Robin (no more requests from powerful servers)
- Least Connections (less connection)
- Weighted Least Connections (less connection and more power).